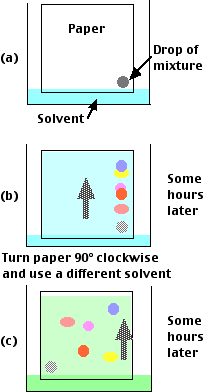
1. Heat insulator - retains heat in the body
2. Lung surfactant - phospholipid
3. Transport substance - lipoproteins
4. Basic nucleus for steroid hormones
5. Energy source - is a purer form that carbohydrate
For more information visit the link below:
associatedcontent.com
About Clinical Chemistry, the determinations of blood constituents like glucose, uric acid, triglycerides, cholesterol, blood gas, enzymology, electrolytes, drugs and the clinical significance of their abnormal values. Deals also with quality assurance and function tests.
AdSense
Tuesday, April 29, 2008
Monday, April 28, 2008
DIABETES MELLITUS
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF ELEVATED BLOOD GLUCOSE
Diabetes Mellitus
When the pancreas produces insufficient insulin or no insulin at all, Diabetes Mellitus results. This is because insulin is responsible in maintaining the normal blood glucose levels by several processes that allow the body’s tissues to absorb glucose and utilize it as energy or store it for future use.
Diabetes Mellitus is characterized by what is called the classical triad, or the three P's - polyuria, polydyipsia and polyphagia. Other symptoms also are hyperglycemia and glycosuria among others. This condition can affect several organs in the body.
For more information visit this site: MedicineNet.com

Diabetes Mellitus
When the pancreas produces insufficient insulin or no insulin at all, Diabetes Mellitus results. This is because insulin is responsible in maintaining the normal blood glucose levels by several processes that allow the body’s tissues to absorb glucose and utilize it as energy or store it for future use.
Diabetes Mellitus is characterized by what is called the classical triad, or the three P's - polyuria, polydyipsia and polyphagia. Other symptoms also are hyperglycemia and glycosuria among others. This condition can affect several organs in the body.
For more information visit this site: MedicineNet.com

Image: FreeDigitalPhotos.net
Saturday, April 19, 2008
LABORATORY TESTS FOR GLUCOSE
Glucose is the most predominant carbohydrate and is the sugar tested in blood sugar
tests. There are certain preparations/precautions before an accurate laboratory test for glucose could be performed.
Whatever method is selected, the Medical Technologist must take the proper precautions in sample collection to prevent glucose utilization by leukocytes.
If the sample is left at room temperature, glucose in sample is reduced 10mg/dL/hour, therefore sample should be refrigerated within 30 minutes after extraction.
2 mg sodium fluoride per mL blood could be also added to prevent glycolysis for 24 hours.
Normal values:
Before meal: 90-130 mg/dL
After meal: < 180 mg/dL
There are Two General Methods for Glucose Detemination:
A. Chemical Methods - oxidation-reduction methods (ferric and cupric), condensation
methods
B. Enzymatic Methods - Hexokinase, Glucose Oxidase
Under the Chemical Methods: ( Alkalike copper reduction methods)
1. Folin-Wu - involves the conversion of phosphomolybdic acid to phosphomolybdenum blue
Reference value: 80-120 mg/dL
Precautions:
* Reagents should be freshly prepared
* Spectrophotometer: wavelength -520 nm
* Deprotienization should be done with the sample- removing of proteins from biologic fluids thru dilution
2 Nelson-Somogyi - involves the conversion of arsenomolybdic acid to arsenomolybdenum blue.
Spectrophotometer: 500-520 nm
3. Neocuproine - involves neocuproine reagent which produces a neocuproine complex.
• Spectrophotometer: 450 nm
4. Shaeffer-Hartmann-Somogyi - involves the use of iodine utilization as an indicator of the amount of glucose in the sample.
Spectrophotometer: 500-520 nm
5. Benedict’s
Reference value: 80-120 mg/dL
Precautions:
* Reagents should be freshly prepared
Chemical Methods (Alkaline Ferric Reduction Method)
1. Hagedorn-Jensen
Precautions:
* Traces of coagulum into the filtrate can cause increase in results.
* The stem of the funnel should have an ample amount of cotton.
Chemical Methods (Condensation Method)
1. Ortho-Toluidine
Gluconeer
Precautions:
* Non-icteric, non lipemic and unhemolyzed serum should be used.
* Patients should not be suffering from galactosemia
* Patients should not be under galactose load
www.freeimages.co.uk
B. Enzymatic Methods
1. Glucose Oxidase Method
2. Hexokinase Method
Reference Values:
* Fasting Serum Glucose: 70-110 mg/dL
* CSF:
Infant: 60-80 mg/dL
Adult: 40-70 mg/dL
* Urine (24 hours): 1-15 mg/dL
Precautions:
* Do not ingest the reagent, toxicity has not been established
* Spectrophotometer: 340 nm
* Use fresh, unhemolyzed serum. Plasma from tubes containing heparin, citrate,
oxalate or EDTA.
* Separate RBC from serum or plasma ASAP
* Glucose in whole blood is decreased 7% per hour.
* Turbid or icteric sera require sample blank
3. Glycosylated Hemoglobin
– HbA1c
Reference value: 4.0-6.0%
Precautions:
* Ample amount of blood- 5ml
* Apply pressure to the puncture site
FBS (Fasting Blood Sugar),the patient must have fasted for 8- 14 hours. This is because a non fasting patient will have an inaccurately increased value because of the effect of the ingested food.
The best anticoagulant in the specimen collection is sodium fluoride. This is because aside from acting as an anticoagulant, it also prevents glycolysis which can decrease inaccurately, the values obtained.
There are other tests like OGTT, (Oral Glucose Tolerance Tests), IGTT (Intravenous Glucose Tolerance Tests), RBS (Random Blood Sugar), 2HPPT ( 2- Hour Post Prandial Test)
tests. There are certain preparations/precautions before an accurate laboratory test for glucose could be performed.
Whatever method is selected, the Medical Technologist must take the proper precautions in sample collection to prevent glucose utilization by leukocytes.
If the sample is left at room temperature, glucose in sample is reduced 10mg/dL/hour, therefore sample should be refrigerated within 30 minutes after extraction.
2 mg sodium fluoride per mL blood could be also added to prevent glycolysis for 24 hours.
Normal values:
Before meal: 90-130 mg/dL
After meal: < 180 mg/dL
There are Two General Methods for Glucose Detemination:
A. Chemical Methods - oxidation-reduction methods (ferric and cupric), condensation
methods
B. Enzymatic Methods - Hexokinase, Glucose Oxidase
Under the Chemical Methods: ( Alkalike copper reduction methods)
1. Folin-Wu - involves the conversion of phosphomolybdic acid to phosphomolybdenum blue
Reference value: 80-120 mg/dL
Precautions:
* Reagents should be freshly prepared
* Spectrophotometer: wavelength -520 nm
* Deprotienization should be done with the sample- removing of proteins from biologic fluids thru dilution
2 Nelson-Somogyi - involves the conversion of arsenomolybdic acid to arsenomolybdenum blue.
Spectrophotometer: 500-520 nm
3. Neocuproine - involves neocuproine reagent which produces a neocuproine complex.
• Spectrophotometer: 450 nm
4. Shaeffer-Hartmann-Somogyi - involves the use of iodine utilization as an indicator of the amount of glucose in the sample.
Spectrophotometer: 500-520 nm
5. Benedict’s
Reference value: 80-120 mg/dL
Precautions:
* Reagents should be freshly prepared
Chemical Methods (Alkaline Ferric Reduction Method)
1. Hagedorn-Jensen
Precautions:
* Traces of coagulum into the filtrate can cause increase in results.
* The stem of the funnel should have an ample amount of cotton.
Chemical Methods (Condensation Method)
1. Ortho-Toluidine
Gluconeer
Precautions:
* Non-icteric, non lipemic and unhemolyzed serum should be used.
* Patients should not be suffering from galactosemia
* Patients should not be under galactose load

www.freeimages.co.uk
B. Enzymatic Methods
1. Glucose Oxidase Method
2. Hexokinase Method
Reference Values:
* Fasting Serum Glucose: 70-110 mg/dL
* CSF:
Infant: 60-80 mg/dL
Adult: 40-70 mg/dL
* Urine (24 hours): 1-15 mg/dL
Precautions:
* Do not ingest the reagent, toxicity has not been established
* Spectrophotometer: 340 nm
* Use fresh, unhemolyzed serum. Plasma from tubes containing heparin, citrate,
oxalate or EDTA.
* Separate RBC from serum or plasma ASAP
* Glucose in whole blood is decreased 7% per hour.
* Turbid or icteric sera require sample blank
3. Glycosylated Hemoglobin
– HbA1c
Reference value: 4.0-6.0%
Precautions:
* Ample amount of blood- 5ml
* Apply pressure to the puncture site
FBS (Fasting Blood Sugar),the patient must have fasted for 8- 14 hours. This is because a non fasting patient will have an inaccurately increased value because of the effect of the ingested food.
The best anticoagulant in the specimen collection is sodium fluoride. This is because aside from acting as an anticoagulant, it also prevents glycolysis which can decrease inaccurately, the values obtained.
There are other tests like OGTT, (Oral Glucose Tolerance Tests), IGTT (Intravenous Glucose Tolerance Tests), RBS (Random Blood Sugar), 2HPPT ( 2- Hour Post Prandial Test)
ORAL GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TESTS
The oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) measures the body's ability to metabolize glucose. This test is used to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes and to determine gestational diabetes in pregnant women.
Patient Preparation:
* Regular diet containing least 150 to 200 grams of carbohydrate per day is
observed for 3 days prior to the test.
* Medications should be referred to the doctor whether to stop or continue taking
them.
* Alcohol and cigarettes are not allowed at least 8 hours before blood collection.
* Strenuous exercise also is to be avoided at least 8 hours before blood collection.
* No unnecessary activities ( doing errands, manual labor) should be done during the
duration of the test.
* The patient is allowed water.
* If the fasting blood sugar is between 100-130 mg/dL, then OGTT is recommended.
Ranges higher than this, FBS is recommended.
* The patient should be ambulatory.
* The test should be performed in a hospital where a resident doctor can respond to
any emergencies.
* For polycystic ovary syndrome, a Glucose tolerance test screening is usually
performed at age 30 and above.
* Urine and fasting blood specimens should be tested first, before proceeding with
the test.
Patient Preparation:
* Regular diet containing least 150 to 200 grams of carbohydrate per day is
observed for 3 days prior to the test.
* Medications should be referred to the doctor whether to stop or continue taking
them.
* Alcohol and cigarettes are not allowed at least 8 hours before blood collection.
* Strenuous exercise also is to be avoided at least 8 hours before blood collection.
* No unnecessary activities ( doing errands, manual labor) should be done during the
duration of the test.
* The patient is allowed water.
* If the fasting blood sugar is between 100-130 mg/dL, then OGTT is recommended.
Ranges higher than this, FBS is recommended.
* The patient should be ambulatory.
* The test should be performed in a hospital where a resident doctor can respond to
any emergencies.
* For polycystic ovary syndrome, a Glucose tolerance test screening is usually
performed at age 30 and above.
* Urine and fasting blood specimens should be tested first, before proceeding with
the test.
Friday, April 18, 2008
CARBOHYDRATES
Image from: Wikimedia.org
Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for the body. Sources of carbohydrates are rice, bread, pasta, corn, and many more. When ingested they are reduced to monosaccharide by the body's biochemical processes.
The most predominant monosaccharide is glucose. Glucose- also known as dextrose- is the sugar tested in the clinical laboratory when a person requests for a blood sugar test.
Blood glucose levels are maintained in the body at 60-100 mg/dL and this level is maintained through the body's homeostatic ability.
When the glucose levels increase the primary hormone that decreases this levels is insulin. On the other hand, the primary hormone that increases glucose levels when it is below normal, is glucagon. Both of these hormones are produced by the pancreas in the beta and alpha cells of the Islets of Langerhans, respectively.
Since blood glucose levels are affected by diet through the food that we eat, fasting is required before a test is performed( except in cases of RBS - Random Blood Sugar).
Fasting hours for 8-12 hours is done prior to the extraction of blood.
In the colorimetric method of glucose determination, visit the link below for full information and example:
Bioassaysys.com
Tuesday, April 15, 2008
LABORATORY MATHEMATICS
There are several methods of expressing concentrations:
1. Percent solutions - W/V (Weight over volume), W/W (weight over weight), V/V(volume over volume)
2. Normality - the gram equivalent weight of a solute per liter of solution.
3. Molarity - the gram molecular weight of a solute per lier of solution.
4. Molality - the gram molecular weight of solute per 1,000 gram of solvent.
1. Percent solutions - W/V (Weight over volume), W/W (weight over weight), V/V(volume over volume)
2. Normality - the gram equivalent weight of a solute per liter of solution.
3. Molarity - the gram molecular weight of a solute per lier of solution.
4. Molality - the gram molecular weight of solute per 1,000 gram of solvent.
Thursday, April 3, 2008
THYROID FUNCTION TESTS
THYROID FUNCTION TESTS
These are laboratory tests that are performed to determine thyroid function.
PRECAUTIONS IN SPECIMEN COLLECTION & HANDLING
•RED TOP OR YELLOW TOP CAN BE USED
•AVOID USE OF LIPEMIC & HEMOLYZED SERUM
•NEWBORNS- FILTER PAPER BLOT CAN BE USED
•FASTING- NOT NEEDED
•SAMPLES CAN BE REFRIGERATED-24 HRS.
•FROZEN FOR 30 DAYS (AVOID REPEATED THAWING)
BLOOD TESTS:
•Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
This is a significant marker for hypothyroidism. an increase in its concentration indicates hypothyroidism and a decrease indicates hyperthyroidism
Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3)
increased concentrations indicate hyperthyroidism
decreased concentrations indicate hypothroidism
•Thyroxine-Binding Globulin. (TBG)
this is the major binding protein of thyroid hormones
Other tests:
rT3, T3U, FTI, FT3, FT4
Stimulation Tests
•-TRH STIMULATION TEST
TRH IS INJECTED INTO THE PATIENT AND THE RESPONSE OF THE PITUITARY GLAND IS OBSERVED.
•TSH STIMULATION TEST
TSH IS GIVEN TO THE PATIENT AND THEN THE REPONSE OF THE THYROID GLAND IS MEASURED.
These are laboratory tests that are performed to determine thyroid function.
PRECAUTIONS IN SPECIMEN COLLECTION & HANDLING
•RED TOP OR YELLOW TOP CAN BE USED
•AVOID USE OF LIPEMIC & HEMOLYZED SERUM
•NEWBORNS- FILTER PAPER BLOT CAN BE USED
•FASTING- NOT NEEDED
•SAMPLES CAN BE REFRIGERATED-24 HRS.
•FROZEN FOR 30 DAYS (AVOID REPEATED THAWING)
BLOOD TESTS:
•Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
This is a significant marker for hypothyroidism. an increase in its concentration indicates hypothyroidism and a decrease indicates hyperthyroidism
Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3)
increased concentrations indicate hyperthyroidism
decreased concentrations indicate hypothroidism
•Thyroxine-Binding Globulin. (TBG)
this is the major binding protein of thyroid hormones
Other tests:
rT3, T3U, FTI, FT3, FT4
Stimulation Tests
•-TRH STIMULATION TEST
TRH IS INJECTED INTO THE PATIENT AND THE RESPONSE OF THE PITUITARY GLAND IS OBSERVED.
•TSH STIMULATION TEST
TSH IS GIVEN TO THE PATIENT AND THEN THE REPONSE OF THE THYROID GLAND IS MEASURED.
THE CATECHOLAMINES
ADRENAL HORMONES
The CATECHOLAMINES are produced and metabolized in the ADRENAL MEDULLA.
The two most common catecholamines are:
1. EPINEPHRINE
2. NOREPINEPHRINE
These catecholamines are also called "EMERGENCY HORMONES" as they increase the ability of the body to respond to stressful situations.
They elevate blood pressure, increase glucose concentration in the blood stream and control a series of biochemical processes.
For more information about the topic visit the link below:
Become Healthy Now
The CATECHOLAMINES are produced and metabolized in the ADRENAL MEDULLA.
The two most common catecholamines are:
1. EPINEPHRINE
2. NOREPINEPHRINE
These catecholamines are also called "EMERGENCY HORMONES" as they increase the ability of the body to respond to stressful situations.
They elevate blood pressure, increase glucose concentration in the blood stream and control a series of biochemical processes.
For more information about the topic visit the link below:
Become Healthy Now
Tuesday, April 1, 2008
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)